How cryptography can be applied to an ICT system and data security.
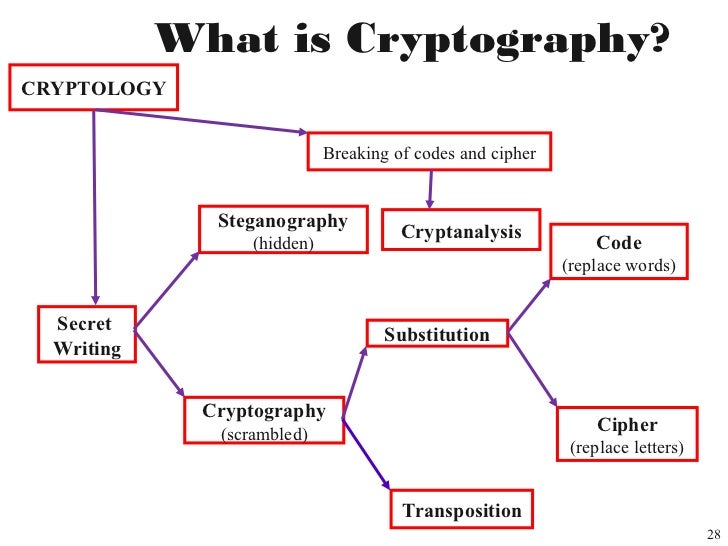 Cryptography is a method of storing and transmitting data in a certain way where only people who are intended to use it, can read and process it. The term is also associated with scrambling plain text (ordinary text) into cipher text (encryption), and then back again (decryption). To decrypt cipher text users will need a key which transforms the cipher text back to the plain text. Cryptography is an effective way of protecting sensitive information as it is stored on media or transmitted through network communication paths.
Cryptography is a method of storing and transmitting data in a certain way where only people who are intended to use it, can read and process it. The term is also associated with scrambling plain text (ordinary text) into cipher text (encryption), and then back again (decryption). To decrypt cipher text users will need a key which transforms the cipher text back to the plain text. Cryptography is an effective way of protecting sensitive information as it is stored on media or transmitted through network communication paths. Public Key Infrastructure.
Public key Infrastructure is a system required to provide public key encryption and digital signature services. Its purpose is to manage keys and certificates, by managing these through a PKI an organisation can establish and maintain a trustworthy networking environment. Certificate Authoroties (CA) such as Verisign issue and manage security credentials and public keys for message encryption. As part of a PKI, the CA checks with the registration authority (RA) to verify information provided by the requester of a digital certificate.
More information on PKI can be found here: